Example 3 A G melodic minor scale Be sure to listen to Example 3 carefully, and notice that the half and wholestep pattern of the melodic minor form of the minor scale is not the same ascending and descending In its descending form, the melodic form of the minor scale is the same as the natural form of the minor scale242 bytes Asharp melodic minor scale ascending and descendingmid 00 s;The G Minor Scales Here are the G Minor Scales the natural minor scale, the melodic minor scale, and the harmonic minor scale Fingerings are included Learn the scales ascending and descending First, try one octave, and then try two octaves (Eventually, you should be able to play each scale with both hands, ascending and descending, four

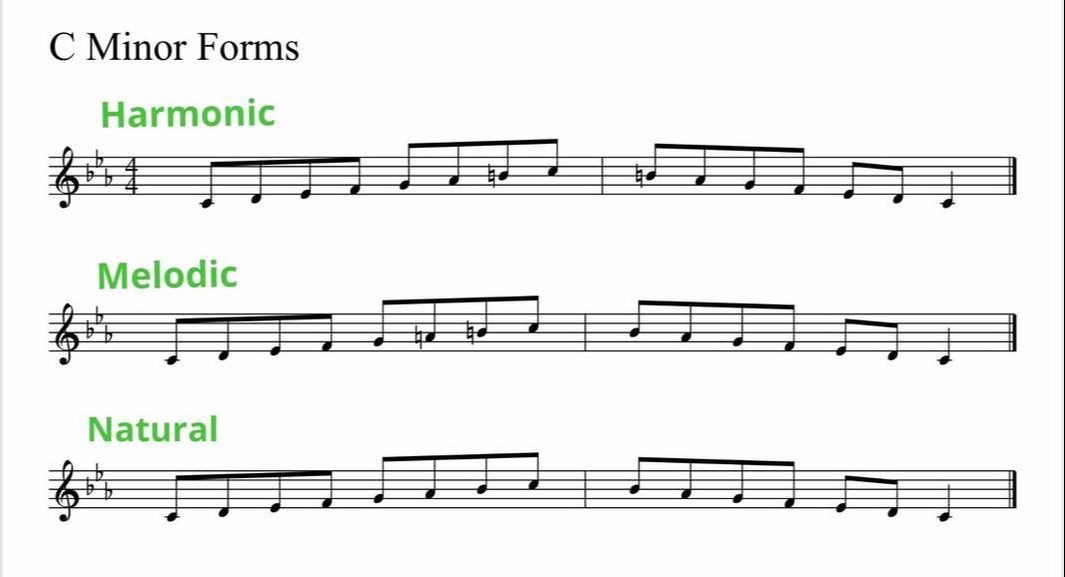
The G Minor Scales
G melodic minor scale descending
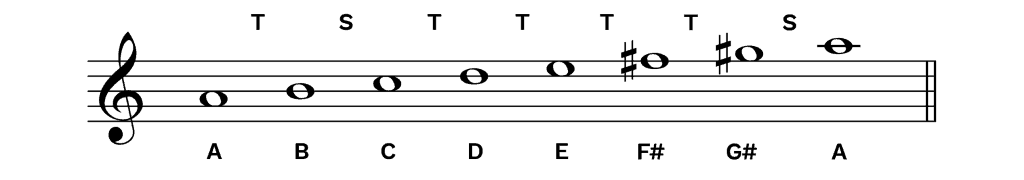
G melodic minor scale descending- When the scale is descending, the melodic minor is the same as the natural minor, eg C, D, Eflat, F, G, A, B, C (ascending)C, Bflat, Aflat, G, F, Eflat, D, C (descending)SCALE STEPS (IN SEMITONES OR HALF STEPS)cdebfgabc'Play Melodic Minor Scale Ascendingcdebfgabbbc'Play Melodic Minor Scale DescendingAlso see minor The ascending A melodic minor scale is A, B, C, D, E, F#, G#, A, whereas the descending melodic minor scale is the same as the natural minor scale A, G, F, E, D, C, B, A The A Melodic Minor scale, ascending and descending, with intervals between each pitch notated as a W (wholestep) or h (halfstep)




Minor Scales 2 And 3 Octave Transposable Patterns Jeffrey Goodman Music
Chromatic Scales that use different letter names for writing ascending notes and descending notes are called Melodic Chromatic Scales The easiest way to write them is to follow these 4 Rules Raise the notes ascending – try to switch to sharps as soon as possible, or use sharps whenever possible, to show an ascending pitch patternThe first mode of the melodic minor scale isthe melodic minor scale In Classical music, you play the 'true' melodic minor scale ascending and the natural minor scale descending But in Jazz, we play the 'true' melodic minor scale both up and down, and call itIn music theory, the term minor scale refers to three scale patterns – the natural minor scale (or Aeolian mode), the harmonic minor scale, and the melodic minor scale (ascending or descending) – rather than just one as with the major scale Musical scores are temporarily disabled Musical scores are temporarily disabled
The melodic minor scale is exactly the same as the natural minor in descending form, but it has different notes in ascending form Going up, the melodic minor scale differs from the natural minor scale in that the sixth scale degree and seventh scale degree are each raised by one semitone, producing natural sixth and natural seventh scale degreesI think you probably mean 'harmonies' rather than 'harmonics' The harmonic minor scale contains an augmented second (3 semitones) whMajor, minor (3 forms), dominant seventh Terms in this set (15) a minor melodic
History Lesson The melodic minor scale is built by raising the 6th and 7th degrees of the natural minor scale (the aolian mode) In the old days the rule of this scale was that while ascending you raised the 6th and 7th scale degrees but when descending you lowered them back to the natural pitchesThis video demonstrates how to calculate melodic minor scalesIt is advisable that viewers watch part 1 initially as this video expands on the concepts discuSince Locrian ♮2 is a melodic minor chord this is basically the melodic minor version of a half diminished sound Since the m7b5 chord is an Em7b5, the corresponding melodic minor scale is G melodic minor and Again the line starts with the G minMaj7 arpeggio, and the target note is the maj7(F#) which is then here the ♮9 over the Em7b5




G Melodic Minor Scale Youtube




Basicmusictheory Com G Melodic Minor Key Signature
Thanks for the request Q How are harmonics impacted while using descending melodic minor scale (theory, music)?There are many examples of this in the writing of Bach, Vivaldi, Quantz, Beethoven almost any prolific "common practice era" composer (ie the Baroque through the Classical and Romantic periods) melodic minor scale The melodic minor scale is the same as the natural minor scale with the exception that the sixth and seventh tones are raised by a semitone ( half step) when the scale is ascending When the scale is descending, the melodic minor is the same as the natural minor, eg See more about modern scale construction in the Appendix




Weekly Workout Building Colorful Chords From The Harmonic And Melodic Minor Scales Acoustic Guitar



Music Theory Scales And E Minor Scale
The melodic minor descending remains untouched as it is exactly the same as a natural minor scale where B♭, E♭, A♭ are all included in the descending scale in accordance with the key signature Major & Natural Minor ScalesG melodic minor (descending) (Guitar Standard tuning) Other names for this scale major, C dorian, D phrygian, Eb lydian, F mixolydian, A locrian Other melodic scales G melodic minor (ascending) Other minor scales G pentatonic minor, G natural minor, Often, when the melody was descending, the old nat min was good to go, so was retained still is in the 'classical' melodic minor scales we find in so many music examsAlthough jazzers tend to have created their own minor 'scale', which tends to use the ascending melodic minor notes rather than the descending ones
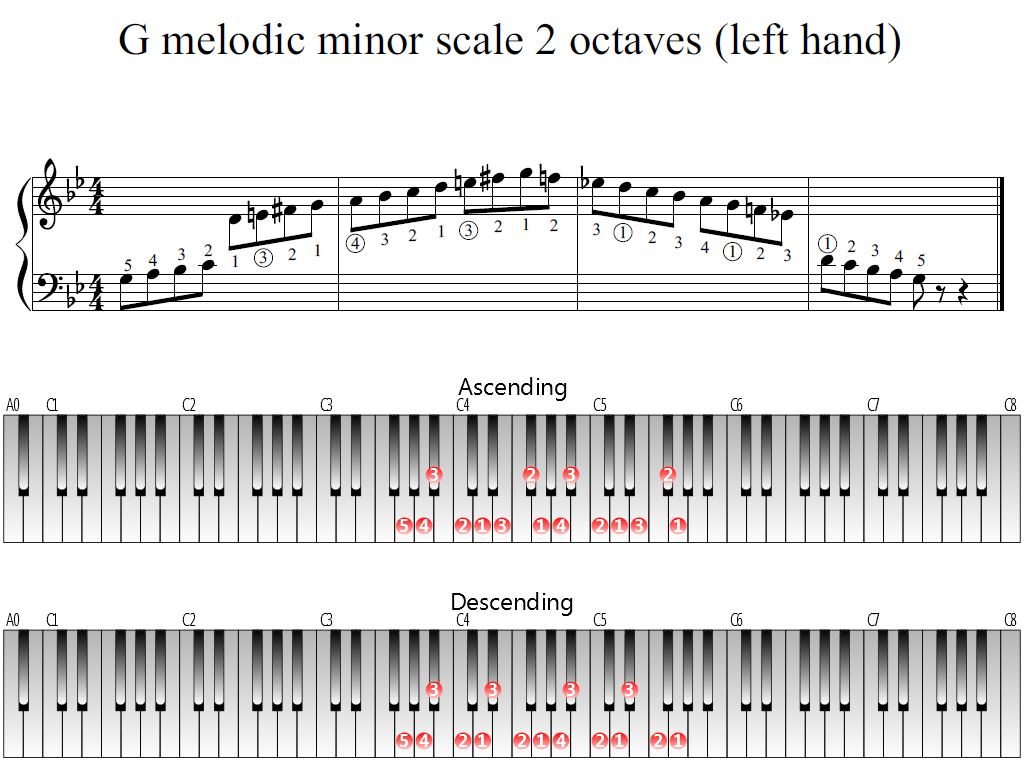




G Melodic Minor Scale 2 Octaves Left Hand Piano Fingering Figures



G Melodic Minor Scale C 01 Craypoe Productions
The melodic minor scale is a seven note scale The melodic minor scale is almost the same as the natural minor with two exception that the sixth and seventh tones are raised by a semitone when the scale is ascending When the scale is descending, the melodic minor is the same as the natural minor Diagram scales F minor In grade three music theory (ABRSM) you need to know two types of minor scales, the harmonic minor and the melodic minor The harmonic minor has the pattern TSTTS3SS (3S = 3 semitones) The melodic minor has one pattern on the way up and another on the way down Ascending (from bottom) TSTTTTS The chords, altered to reflect the melodic minor notes drawn out So (The parent melodic minor being the system from the second degree of the original major key For example A mel min is from the second degree chord of the major key of G) The main chords over which Melodic Minor is most effective (Function within a Major key as 7th chords)




The Melodic Minor Scale And Modes Chapter 1 The Melodic Minor Scale And Its Pdf



How To Use The Melodic Minor Scale
The jazz minor scale is a derivative of the melodic minor scale, except only the ascending form of the scale is usedAs the name implies, it is primarily used in jazzIt may be derived from the major scale with a minor third, making it a synthetic scale, and features a dominant seventh chord on the fifth degree (V) like the harmonic minor scaleScales in the key of G G major G natural minor G harmonic minor G melodic minor G major pentatonic G minor pentatonic G chromaticNotes in the Eflat melodic minor scale Ascending E♭, F, G♭, A♭, B♭, C, D Descending E♭, D♭, C♭, B♭, A♭, G♭, F Scale Formula Ascending W, H




Basicmusictheory Com G Melodic Minor Scale



The Melodic Minor Scale
The melodic scale above has two triads which are capable of functioning as tonics c minor and G major, so these are the tonics of the two tonally effective modes of the melodic scale the (ascending) melodic minor scale and the (descending) melodic major scale Both of these scales can be understood to be melodic "improvements" of the harmonic minor and harmonic major scalesGsharp melodic minor scale classical descending This step shows the notes when descending the Gsharp melodic minor scale, going from the highest note sound back to the starting note, using the natural minor scale descending notes242 bytes Asharp natural minor scale ascending and descendingpng 985 × 126;



The Minor Scales Natural Harmonic And Melodic Hello Music Theory




Why The Ascending Form Of The Melodic Minor Scale Differs From Its Descending Form Hear And Play Music Learning Center
The descending version of the scale contains the same notes as the natural minor scale, so F# and G# are lowered to F and G Deriving the Melodic Minor Scale from the Major Scale The ascending form of the melodic minor scale can also be derived by lowering the third degree of any major scale by a half step3 Melodic Minor Scale The Melodic Minor Scale is the same as the natural minor scale but with a chromatically raised sixth and seventh degree ascending and restored to its normal pitch descending (natural minor)You might find that the harmonic minor scale is a bit angular at the top of the scale to write smooth melodies This is where the melodic minor scale comes




Why Do The Notes Of Melodic Minor Scale Change When You Play It In Descending Order Music Practice Theory Stack Exchange




Are Melodic Minor And Jazz Melodic Minor The Same Scale Quora
Minor scales are as old as Western music itself All styles of music use minor scales to produce melodies, riffs, and chord progressions Minor Scale Guide Natural, Harmonic, and Melodic Minor Scales 21 MasterClassThe descending half of the melodic minor scale is identical to that of the natural minor scale Step 8 – 7 (a – g) whole tone Step 7 – 6 (g – f) whole tone Step 6 – 5 (f – e) semitone Step 5 – 4 (e – d) whole tone Step 4 – 3 (d – c) whole toneAsharp harmonic minor scale ascending and descendingmid 00 s;




The Foundations Scale Steps And Scales




The Melodic Minor Scale Signature Sound
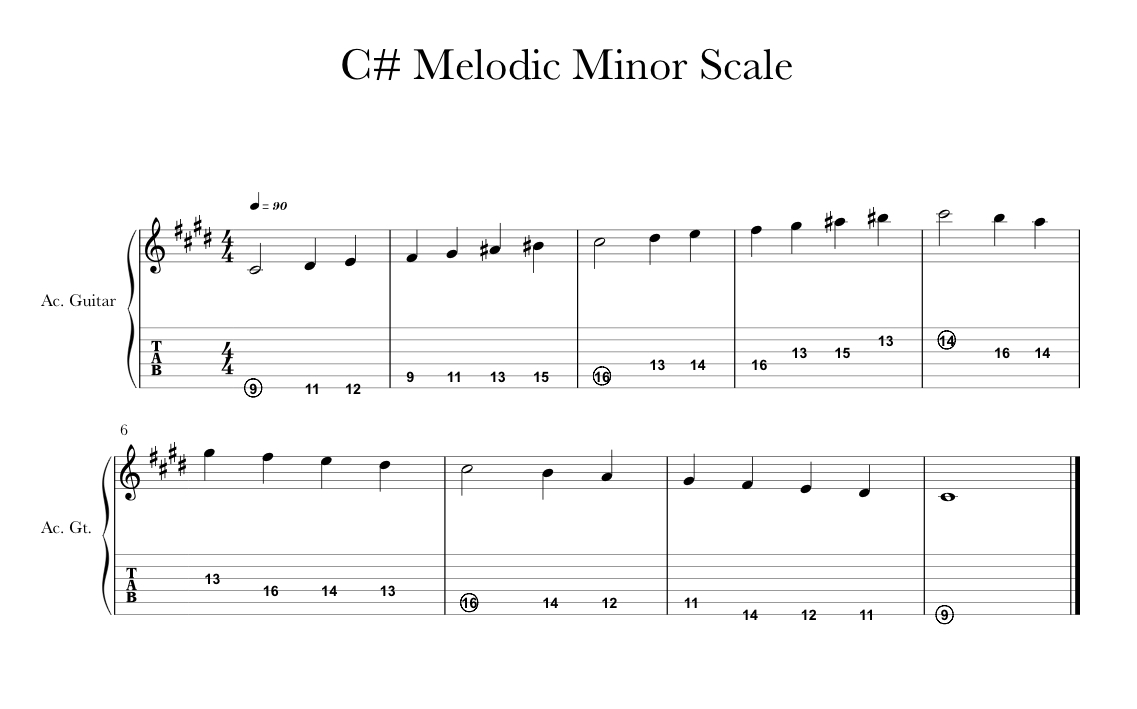
For the melodic minor scale, you raise the sixth and seventh notes of a scale by a half step as you go up the scale and then return to the natural minor as you go down the scale The notes of the C melodic minor scale ascending are C, D, Eb, F, G, A, B, C The notes of the C melodic minor scale descending are C, D, Eb, F, G, Ab, , C (CHalf step intervals occur between scale degrees 23 and 78 of the melodic minor scale The interval of a Whole step occurs between all other scale degrees Most theory books state that the melodic minor scale is different when ascending than when descending (The descending form of the melodic minor scale is the same as natural minor) Melodic Minor Scale The melodic minor scale raises the 6th and 7th notes of the natural minor scale when you are playing in ascending order When the melodic minor scale is played in descending order, the notes of the scale are same as the natural minor




G Major Melodic Scale Piano Shakal Blog



1
In reality, the Melodic Minor scale (raised 6th and 7th scale degrees) may be implemented when ascending and descending (see ex 2);In Classical music theory the melodic minor and natural minor are combined into one scale The melodic minor is used when ascending the scale, the natural minor is used when descending the scale Audio 3 In the past the semitone downward step from tonic to 7th (C B) was considered too harsh a sound for a minor mood3 KB Amollmelodpng 1,654 × 1;



Untitled




The Minor Scale And Its Natural Harmonic And Melodic Forms Spinditty
The melodic minor scale is a seven note scale The melodic minor scale is almost the same as the natural minor with two exception that the sixth and seventh tones are raised by a semitone when the scale is ascending When the scale is descending, the melodic minor is the same as the natural minorThe Melodic Minor Scale differs from the Natural Minor Scale by the sixth and seventh notes, which are raised one semistep This scale is kind of peculiar since it is sometimes played differently ascending and descending Jazz The sixth and seventh notes are always raised, exactly as the pictures below illustrate Personally, I don't know why anybody would practice the descending melodic minor scale with the b6 and b7, because then you are just practicing the natural minor descending I would practice the raised 6th and 7th when descending also Also, I don't like practicing the harmonic minor scale either, because the raised 7th is for harmonic reasons




4 4 Minor Keys And Scales




Melodic Minor Scale Musipedia
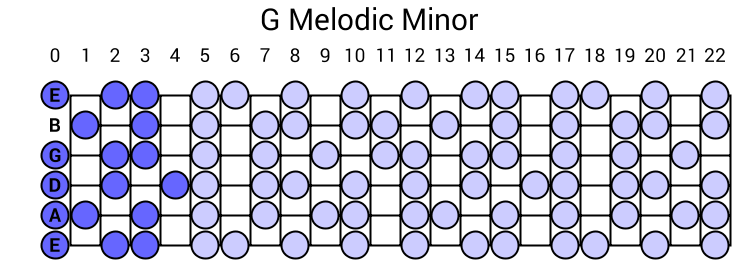
The ascending melodic minor scale is identical to the natural minor scale except for the addition of raised sixth and seventh scale degrees, but the descending scale is a simple natural minor scale, meaning that scale degrees 6 and 7 each revert down a halfstep in the descending scaleThe notes of the G melodic minor scale descending are G, A, B♭, C, D, E♭, and F The formula for a melodic minor scale is WHWWWWH The descending formula is the natural minor scale formula backwards Melodic G Minor Scale IntervalsThe melodic minor scale is the only traditional scale in European music that its descending form is different from the ascending



Minor Scales Sabetmusic



Scales Clairnote Sn Music Notation
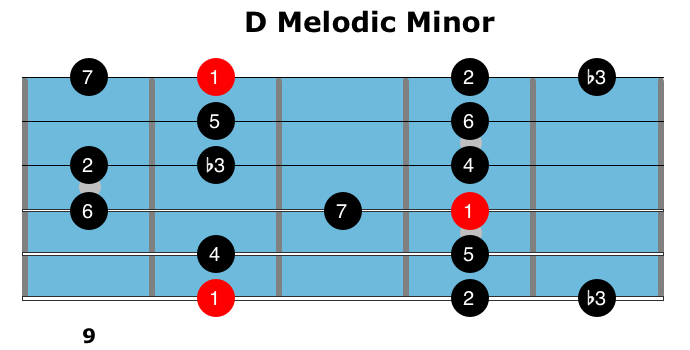
The tablature and standard musical notation for the scale will be shown below Other names for this scale major , C dorian , D phrygian , Eb lydian , F mixolydian , A locrian Other minor scales G pentatonic minor , G harmonic minor , G melodic minor (ascending) , G melodic minor (descending)



G Melodic Minor Scale



2




Music Keys Page 2 The Cello Companion




File G Melodic Minor Scale Ascending And Descending Png Wikipedia




The G Minor Scales




Why Do The Notes Of Melodic Minor Scale Change When You Play It In Descending Order Music Practice Theory Stack Exchange



1




Theory Blog Melodic Minor Scale



Jazclass Jazz Scales Lesson Melodic Minor Scale In All Keys




File G Sharp Natural Minor Scale Ascending And Descending Png Wikipedia
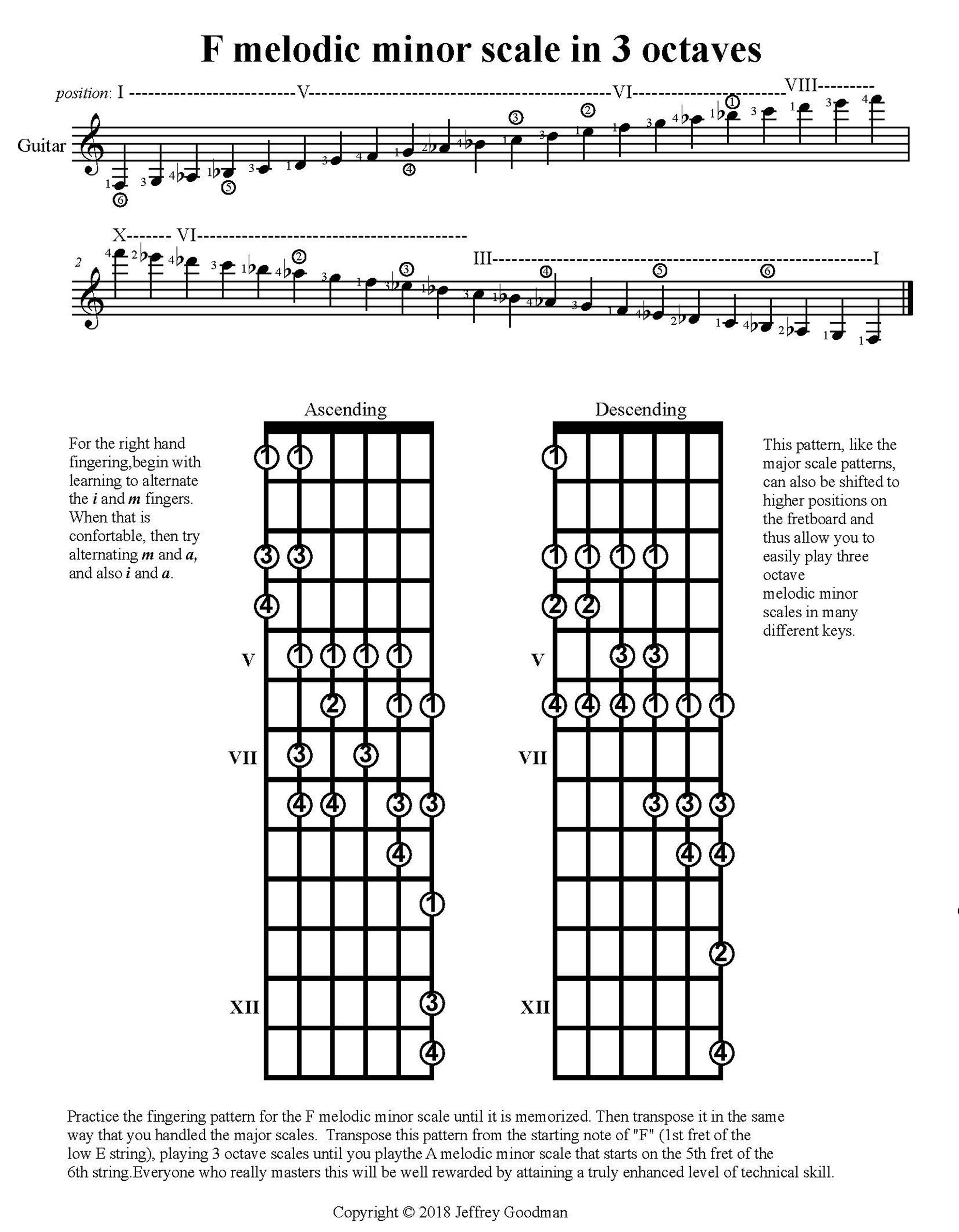



Minor Scales 2 And 3 Octave Transposable Patterns Jeffrey Goodman Music




Minor Scales 2 And 3 Octave Transposable Patterns Jeffrey Goodman Music
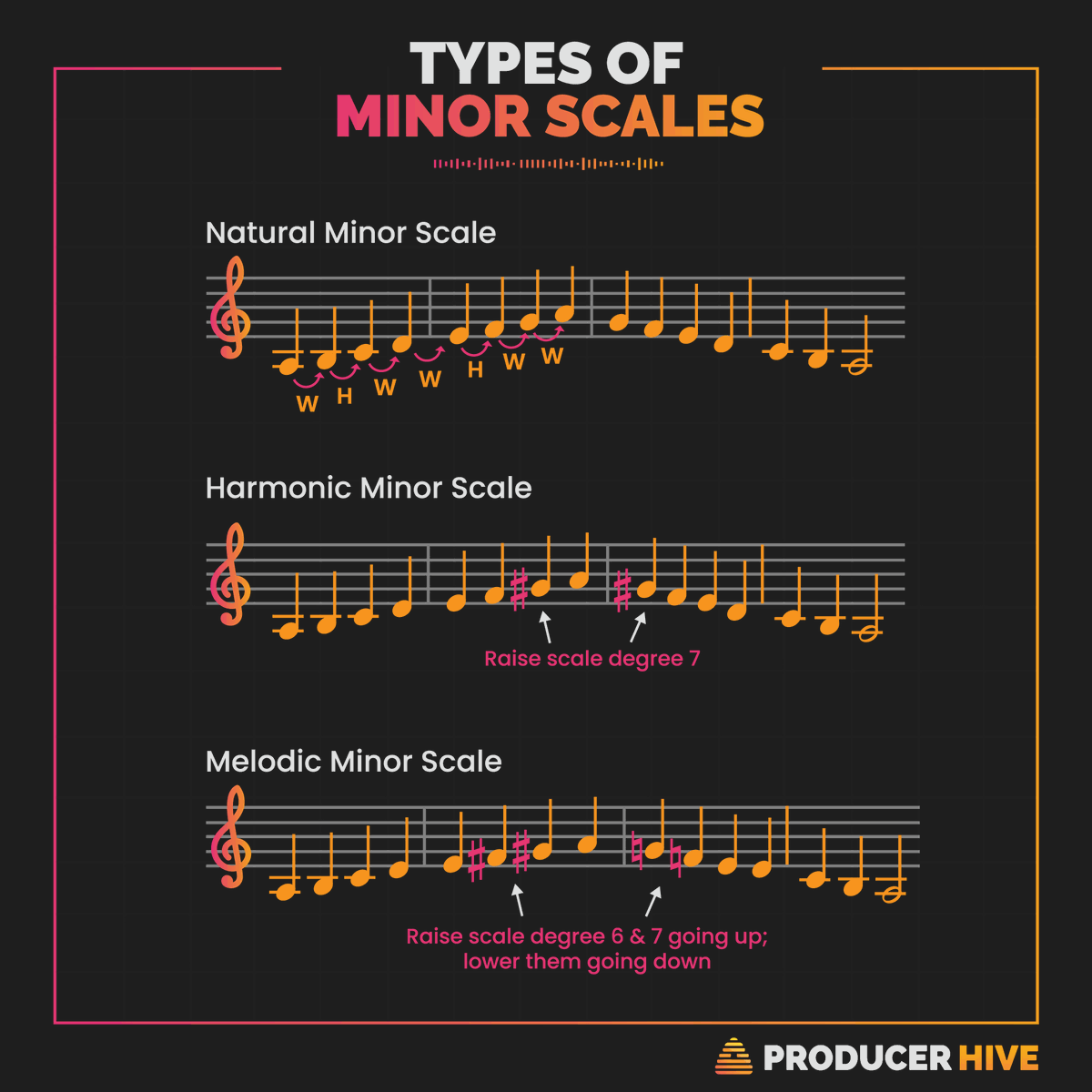



All About The Melodic Minor Scale
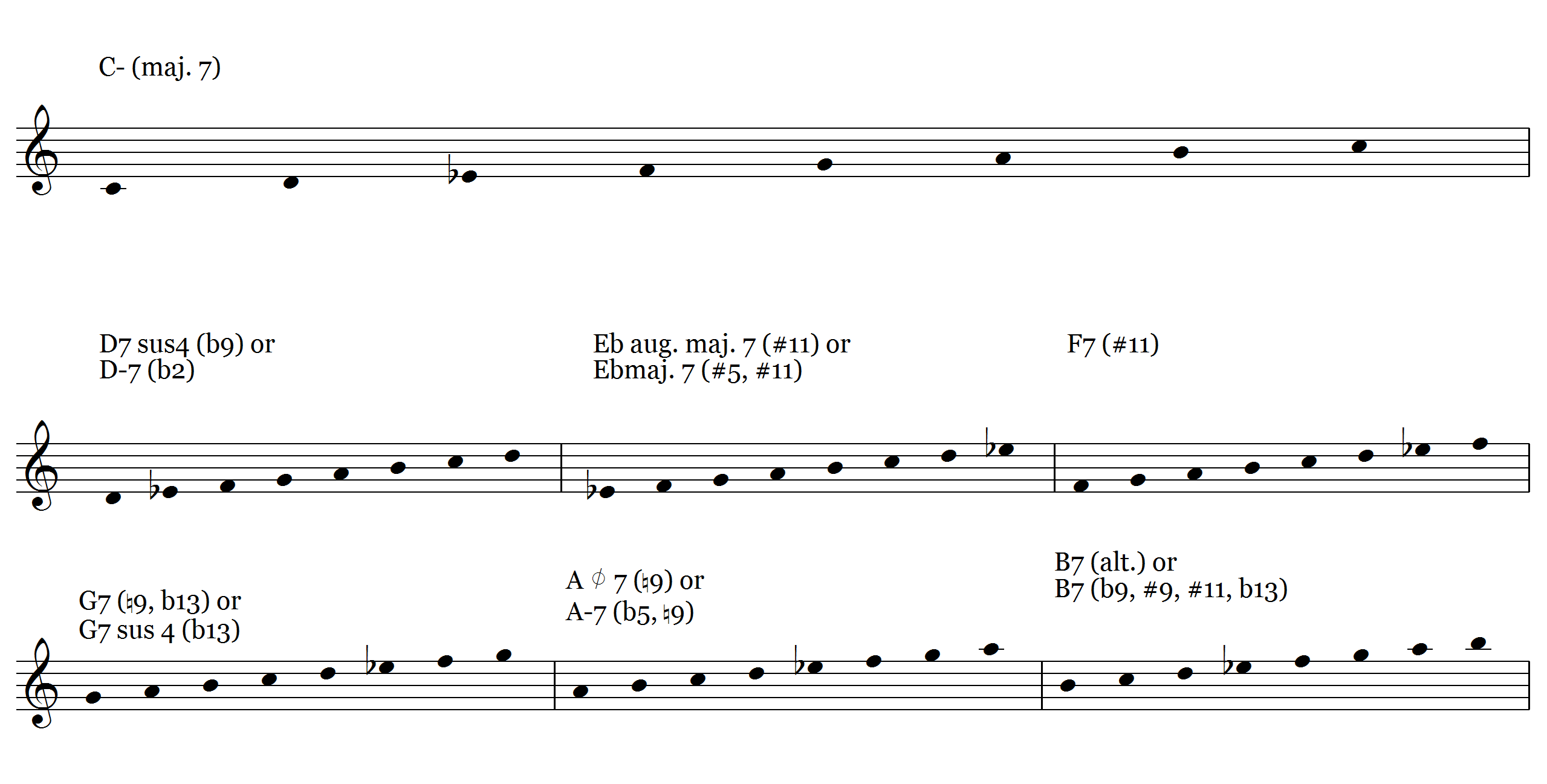



Ljs 86 7 Chords You Can Play The Melodic Minor Scale Over Learn Jazz Standards
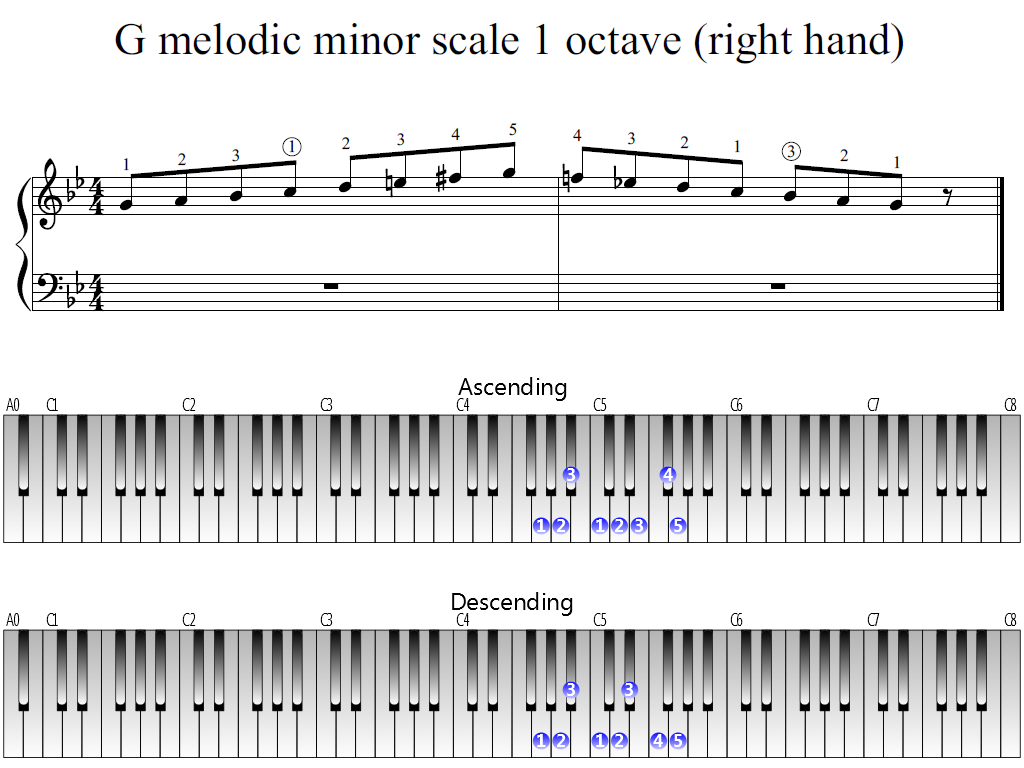




G Melodic Minor Scale 1 Octave Right Hand Piano Fingering Figures



G Melodic Minor Scale For Piano
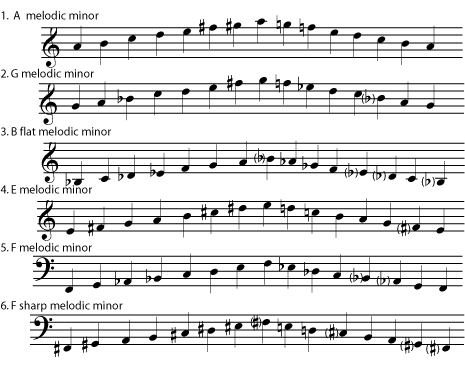



Minor Music Scales Natural Melodic Harmonic Minors



The G Minor Scale Natural Harmonic And Melodic Notes Chords And More




The Minor Scales Natural Harmonic And Melodic Hello Music Theory
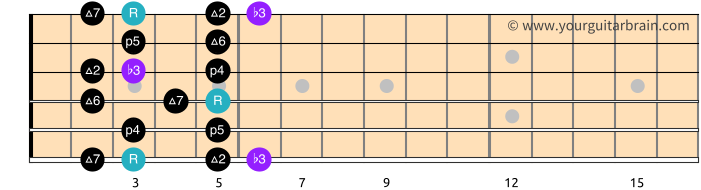



Melodic Minor Scale 5 Patterns Best Guitar Scales To Learn




Melodic Minor Scale




Why Do The Notes Of Melodic Minor Scale Change When You Play It In Descending Order Music Practice Theory Stack Exchange
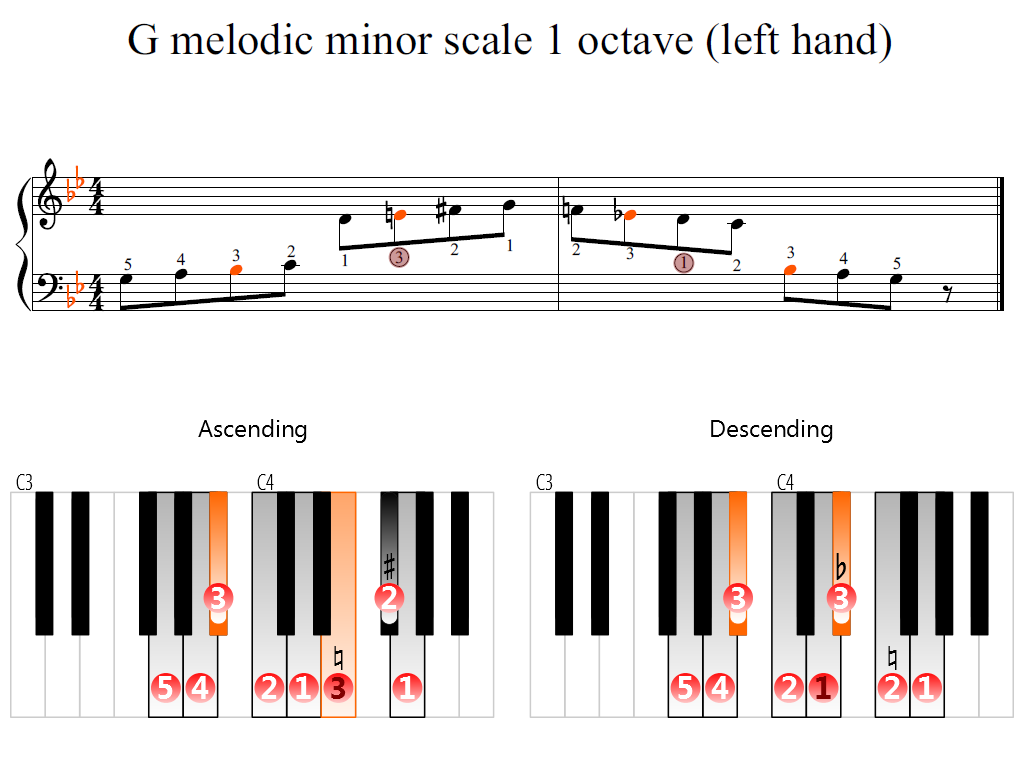



G Melodic Minor Scale 1 Octave Left Hand Piano Fingering Figures




Melodic Minor Scale
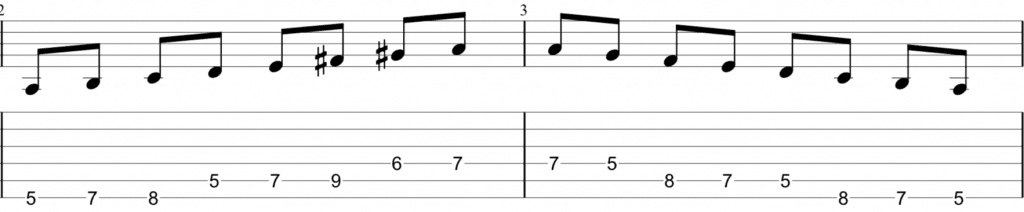



Guitar Practice Melodic Minor Scale Life In 12 Keys



The G Minor Scale Natural Harmonic And Melodic Notes Chords And More




Ljs 86 7 Chords You Can Play The Melodic Minor Scale Over Learn Jazz Standards



Melodic Minor Scale Ricmedia Guitar



1



Why The Ascending Form Of The Melodic Minor Scale Differs From Its Descending Form Hear And Play Music Learning Center




The Minor Scales Music Theory Academy




F Melodic Minor Scale Note Information And Scale Diagrams For Guitarists



Ap Chapter 5 Minor Keys And The Diatonic Modes Amanwarrenmusic Com



Lesson 39 Melodic Minor Scale Epianostudio




Basicmusictheory Com G Melodic Minor Scale



1



G Sharp Melodic Minor Scale C 01 Craypoe Productions
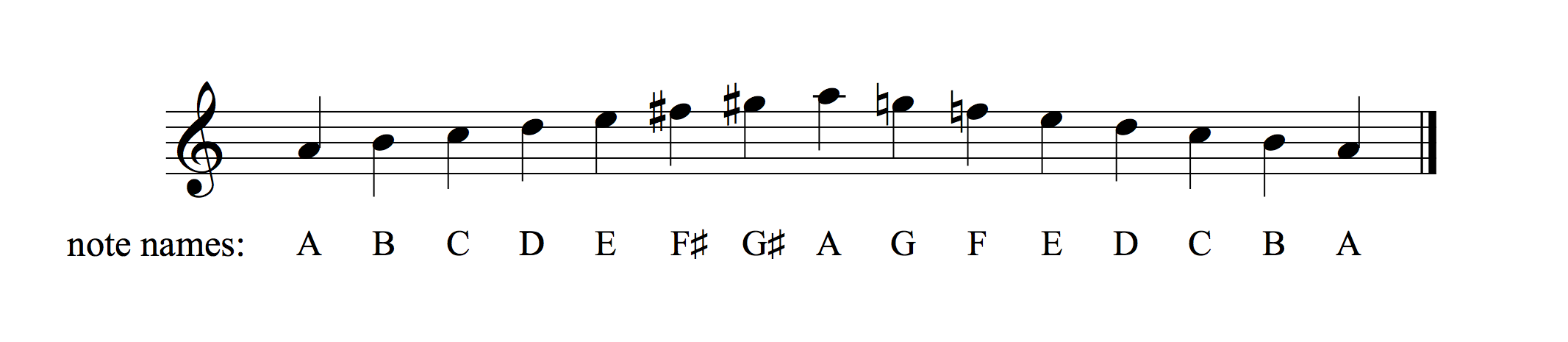



Music Crash Courses



Untitled




File G Sharp Melodic Minor Scale Ascending And Descending Png Wikimedia Commons




Music Theory For Producers Harmonic Field Creating Tracks




The Minor Scales Music Theory Academy




Discover What Is The Famous Piano Scale All About Learn Piano Chords Pro




Relative Majors And Minors How To Work Out Minor Scales On The Piano Ruth Pheasant Piano Lessons




Melodic Minor Scales Shapes Patterns Theory Guitar Kitchen



Jazclass Jazz Scales Lesson Melodic Minor Scale In All Keys



Relative Majors And Minors How To Work Out Minor Scales On The Piano Ruth Pheasant Piano Lessons




Melodic Minor Scale Using Solfege Youtube




Basicmusictheory Com G Melodic Minor Scale



2




Study Keys Level 2



Soprano Recorder Scales G Melodic Minor Scale




Minor Scales Scale Degrees And Key Signatures Open Music Theory



The Minor Scales And Chords Portland Piano Lab




Basicmusictheory Com G Melodic Minor Scale




G Melodic Minor Scale For Piano Make Better Music
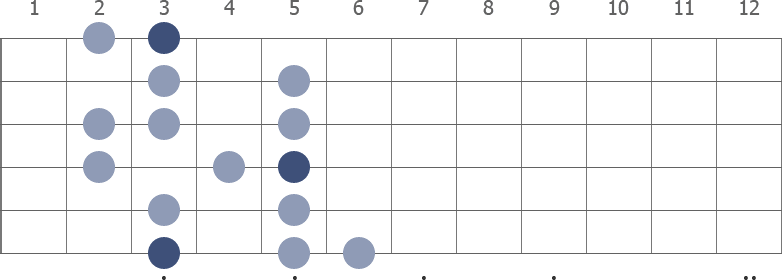



G Melodic Minor Guitar Scale
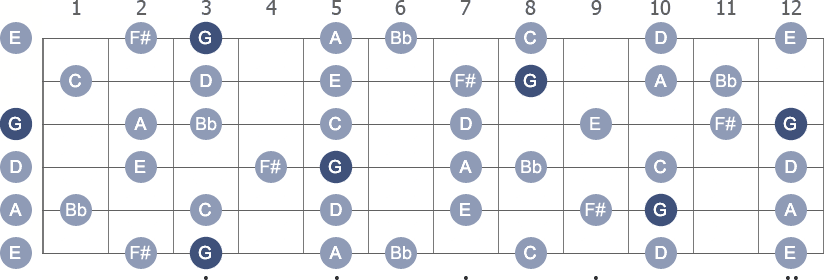



G Melodic Minor Guitar Scale




Melodic Minor For 8 String Scales Modes
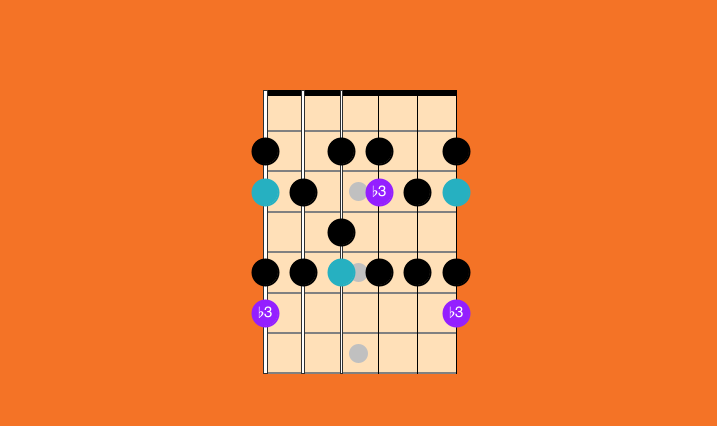



Melodic Minor Scale 5 Patterns Best Guitar Scales To Learn



D Minor Scale Natural Harmonic And Melodic




What Makes The Melodic Minor Scale So Melodic Premier Guitar




Why Are There 3 Minor Scales School Of Composition




G Minor Scale Music Theory



Scales Clairnote Sn Music Notation




Why Do The Notes Of Melodic Minor Scale Change When You Play It In Descending Order Music Practice Theory Stack Exchange



The G Minor Scale Natural Harmonic And Melodic Notes Chords And More




Study The Minor Scale




Basicmusictheory Com A Flat Melodic Minor Scale




Music Theory Minor Scales



Melodic Minor Scale Guide For Jazz Guitar Jamie Holroyd Guitar Jamie Holroyd Guitar




Basicmusictheory Com G Melodic Minor Scale




Why Are There 3 Minor Scales School Of Composition
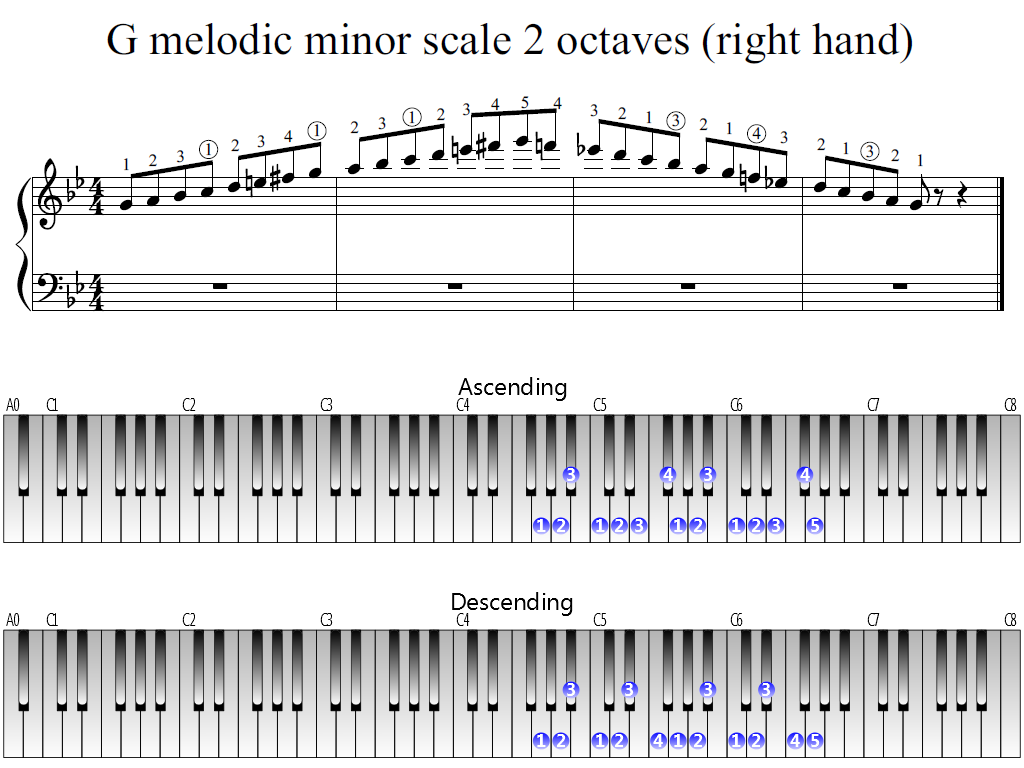




G Melodic Minor Scale 2 Octaves Right Hand Piano Fingering Figures




Music Theory Minor Scales




How To Play A Melodic Minor Scale Pianotv Net
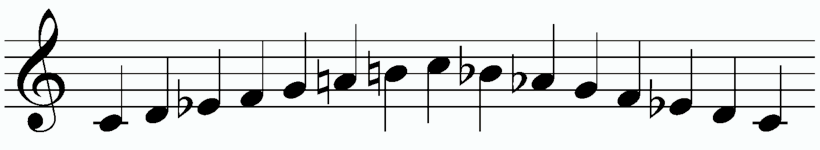



Melodic Minor Scale Musipedia
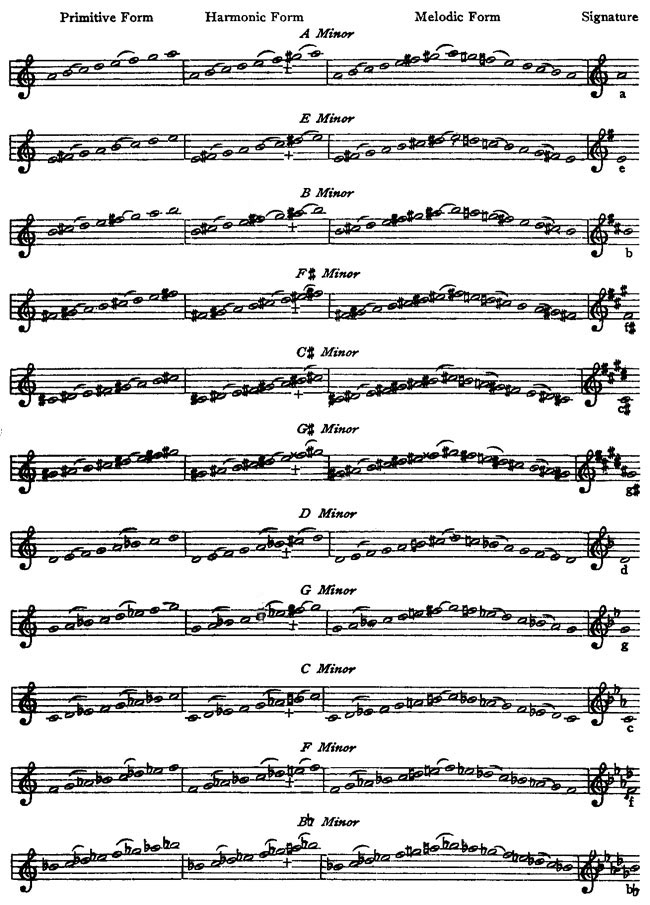



Music Notation And Terminology By Karl W Gehrkens



Minor Scales Part 3 Melodic Minors Youtube



Melodic Minor Scale Ricmedia Guitar



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿